Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and ulcerative colitis (UC) are two chronic, autoimmune conditions that affect different parts of the body but share common underlying mechanisms. While RA primarily targets the joints, UC affects the digestive tract. Despite these differences, both diseases involve the immune system attacking healthy tissues, causing inflammation, pain, and long-term complications if not managed properly. Understanding the connection between RA and UC can help individuals recognize symptoms early, seek appropriate treatment, and live a healthier, more comfortable life.
Jaksure 5 Tablet is a prescription medication containing Tofacitinib 5 mg, a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor. It is primarily used to treat autoimmune and inflammatory conditions by modulating the immune response.
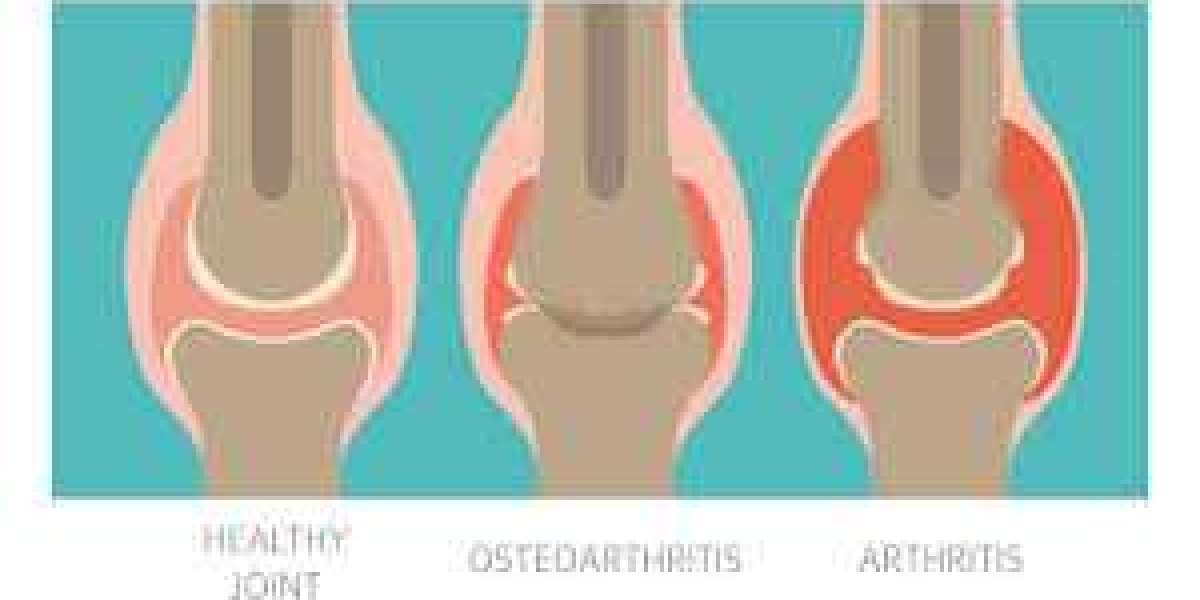
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints. In RA, the immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium—the lining of the joints—causing painful inflammation. Over time, this can lead to joint damage, deformity, and loss of function.
Common Symptoms of RA:
Swollen, tender, and stiff joints
Morning stiffness lasting more than 30 minutes
Fatigue and low-grade fever
Symmetrical joint pain (affecting both sides of the body)
Decreased range of motion
RA commonly affects smaller joints first (fingers, wrists, toes) and can progress to larger joints. It can also involve other organs such as the lungs, eyes, and heart, making it a multi-system disease.
What is Ulcerative Colitis (UC)?
Ulcerative colitis is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes chronic inflammation and ulcers in the innermost lining of the colon and rectum. The exact cause of UC is unknown, but it is believed to result from an abnormal immune response, possibly triggered by environmental factors or gut bacteria in genetically predisposed individuals.
Common Symptoms of UC:
Frequent, bloody diarrhea
Abdominal pain and cramping
Urgency to have a bowel movement
Weight loss and fatigue
Rectal bleeding and mucus in stool
UC symptoms may come and go, with periods of flares and remission. In severe cases, it can lead to complications like colon damage, increased cancer risk, or the need for surgery.
The Autoimmune Connection: RA and UC
Both RA and UC are autoimmune diseases, meaning the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues. People with one autoimmune disease are at a higher risk of developing another. This explains why some individuals may experience both RA and UC, either at the same time or years apart.
Shared characteristics of RA and UC include:
Chronic inflammation driven by an overactive immune response
Genetic susceptibility
Systemic symptoms, such as fatigue and weight loss
Periods of remission and flare-ups
In some cases, medications used to treat one condition may help the other. For instance, biologic drugs like TNF inhibitors (e.g., infliximab, adalimumab) are effective in treating both RA and UC by blocking inflammatory signals.
Managing Life with RA and UC
Living with one or both of these conditions requires a comprehensive and individualized treatment plan.
Medical Management:
RA treatments: DMARDs, biologics, corticosteroids, NSAIDs
UC treatments: Aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, immunomodulators, biologics
Regular monitoring: Blood tests, colonoscopies, and imaging
Lifestyle Strategies:
Anti-inflammatory diet: Emphasize fruits, vegetables, omega-3 fatty acids, and whole grains
Regular exercise: Improves joint flexibility and reduces stress
Stress management: Mindfulness, yoga, or therapy can reduce flares
Adequate sleep: Essential for immune regulation and recovery
Support and Education:
Joining support groups and staying informed about the latest research can empower patients and improve mental health. Coordinating care with a rheumatologist and a gastroenterologist is important for those with both conditions.
Conclusion
Rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis may target different parts of the body, but they share a common thread: an overactive immune system that causes chronic inflammation and discomfort. With early diagnosis, personalized treatment, and lifestyle adjustments, many people with RA and UC can lead active, fulfilling lives. If you're experiencing persistent joint pain or digestive symptoms, it's essential to consult a healthcare provider to get the right diagnosis and start effective treatment.