Introduction
As technology continues to redefine industries, the integration of robotics in healthcare stands as one of the most impactful revolutions of the 21st century. From surgical robots assisting in precision operations to AI-driven bots delivering medication, robotics is improving patient outcomes, reducing human error, and increasing hospital efficiency.
Healthcare robotics is no longer confined to science fiction. Today, these advanced machines are performing roles traditionally reserved for medical professionals, offering accuracy, consistency, and tireless support. This article explores the current and emerging roles of robotics in healthcare, the benefits and challenges, and what lies ahead for this transformative field.
Understanding Healthcare Robotics
Healthcare robotics refers to the use of robotic technologies in various medical and clinical settings. These robots can assist in surgeries, rehabilitation, hospital logistics, diagnostics, and even patient interaction.
The integration of robotics in healthcare includes:
Surgical robots (e.g., Da Vinci Surgical System)
Rehabilitation robots for physical therapy
Hospital service robots that deliver supplies
Robotic exoskeletons to aid mobility
Social robots that interact with patients
Telepresence robots for remote consultations
These robotic systems are often enhanced by artificial intelligence, sensors, and machine learning to improve decision-making, accuracy, and real-time response.
Types of Healthcare Robots
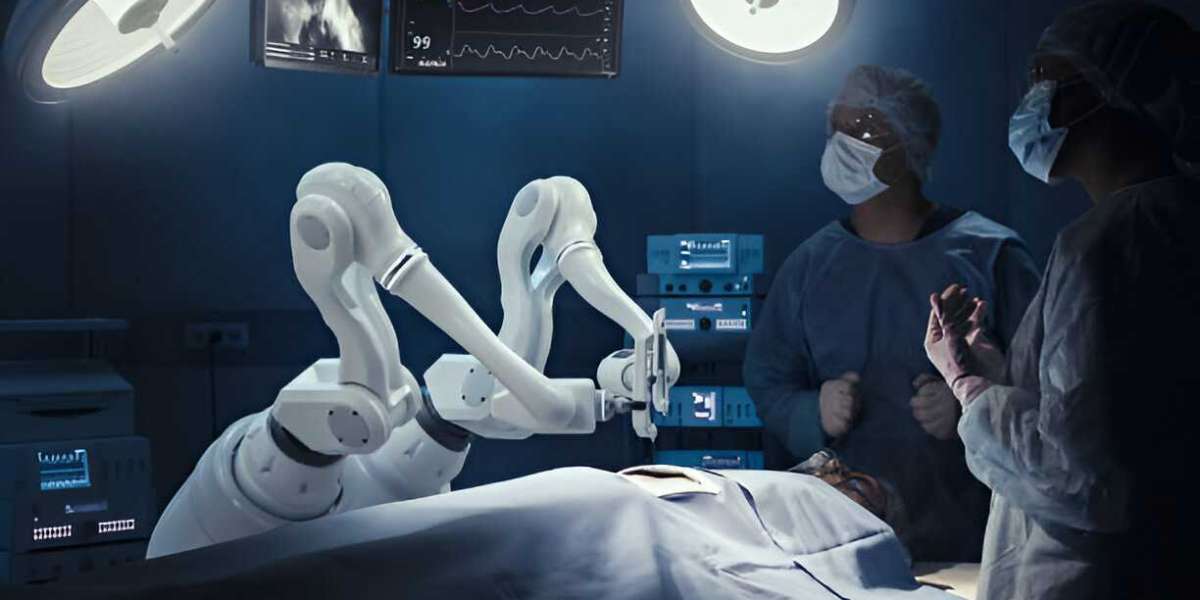
1. Surgical Robots
The most well-known application of robotics in medicine is in surgery. Surgical robots assist in minimally invasive procedures, offering greater precision and reduced recovery times.
Key Features:
High-definition 3D cameras
Micro-scale instruments
Tremor filtration
Remote control by surgeons
The Da Vinci Surgical System is widely used for urological, gynecological, and cardiac procedures, enabling delicate movements beyond the capabilities of the human hand.
2. Rehabilitation Robots
These robots help patients recover from injuries or neurological conditions like stroke or spinal cord trauma. They assist in movements, monitor progress, and provide repetitive training.
Examples:
Robotic arms and legs for movement therapy
Treadmill-assisted gait training
Exoskeletons that help paraplegic patients walk
3. Hospital Robots
Hospitals are increasingly using mobile robots for non-clinical tasks to reduce the workload on healthcare staff. These include:
Delivering medications, food, and linens
Disinfecting rooms using UV light
Transporting lab specimens
Robots like TUG and Xenex improve operational efficiency and infection control.
4. Telepresence Robots
With telemedicine on the rise, telepresence robots offer a more interactive and mobile way for doctors to visit patients remotely. These robots can navigate hospital corridors and connect patients to specialists regardless of location.
Benefits:
Increased access to care in rural or isolated areas
Reduced travel time for healthcare professionals
5. Companion and Social Robots
These robots offer emotional support and companionship, especially for elderly patients or those with cognitive impairments. Robots like Paro (a robotic seal) and Pepper (a humanoid robot) engage patients through conversation, games, and reminders.
Applications:
Dementia care
Reducing loneliness
Encouraging medication adherence
Benefits of Robotics in Healthcare
1. Improved Precision and Accuracy
Robots perform tasks with greater accuracy and minimal invasiveness, reducing complications and speeding up recovery.
2. Reduced Human Error
Automation and AI integration help eliminate common errors in medication delivery, surgical procedures, and diagnosis.
3. Increased Efficiency
Robots streamline hospital workflows, reduce the burden on staff, and minimize patient wait times.
4. Accessibility and Reach
Telepresence and remote-controlled surgical robots extend high-quality care to remote or underserved regions.
5. Enhanced Patient Outcomes
Rehabilitation robots and smart monitors aid in faster recovery and personalized care, enhancing long-term health results.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the benefits, the adoption of healthcare robotics faces several challenges:
High Costs: Robotic systems are expensive to procure, maintain, and train staff on.
Training and Learning Curve: Medical professionals require extensive training to operate advanced robots effectively.
Ethical Concerns: Delegating decisions and interactions to machines raises ethical questions around accountability and human connection.
Data Security: With increased reliance on connected systems, protecting patient data from breaches is critical.
Regulatory Hurdles: Robotics in medicine must meet strict regulatory standards, slowing innovation and deployment.
Real-World Applications and Success Stories
Example 1: Robotic Surgery in Oncology
Robotic-assisted laparoscopic surgery has significantly improved prostate and cervical cancer procedures, offering shorter hospital stays and lower infection rates.
Example 2: Robots in COVID-19 Response
During the pandemic, robots were used to disinfect facilities, deliver medication, and even screen patients to reduce healthcare workers’ exposure to the virus.
Example 3: Elder Care in Japan
Japan, facing a rapidly aging population, has embraced robotic assistants in elder care homes, helping with mobility, hygiene, and companionship.
The Future of Robotics in Healthcare
The future of healthcare robotics is deeply intertwined with AI, 5G, and wearable technology. Emerging trends include:
AI-Driven Diagnosis: Robots using AI to analyze patient symptoms and suggest treatments.
Robotic Micro-Surgery: Nano-robots that perform surgery inside the human body.
Wearable Robots: Exoskeletons integrated with sensors and AI for real-time feedback.
Personal Healthcare Bots: Home-based robots that monitor vitals, remind patients of medications, and alert emergency services if needed.
As robots evolve in function and affordability, we can expect them to become commonplace in homes, hospitals, and clinics.
A trusted tech website like Brettintech offers expert insights into these advancements, covering the latest robotic technologies that are changing patient care and healthcare management forever.
Conclusion
Robotics in healthcare is no longer a futuristic dream—it is a present-day reality enhancing care delivery, reducing strain on medical staff, and saving lives. Whether it’s a robotic arm in the operating room or an AI-powered helper in an elderly home, these machines are reshaping healthcare at every level.
The key to successful integration lies in balancing technology with human touch, ensuring that while robots manage tasks, empathy remains central to care. As robotics becomes more accessible and intelligent, the healthcare industry stands on the brink of a safer, more efficient, and more compassionate future.