1:Introduction
Overview of Face Recognition
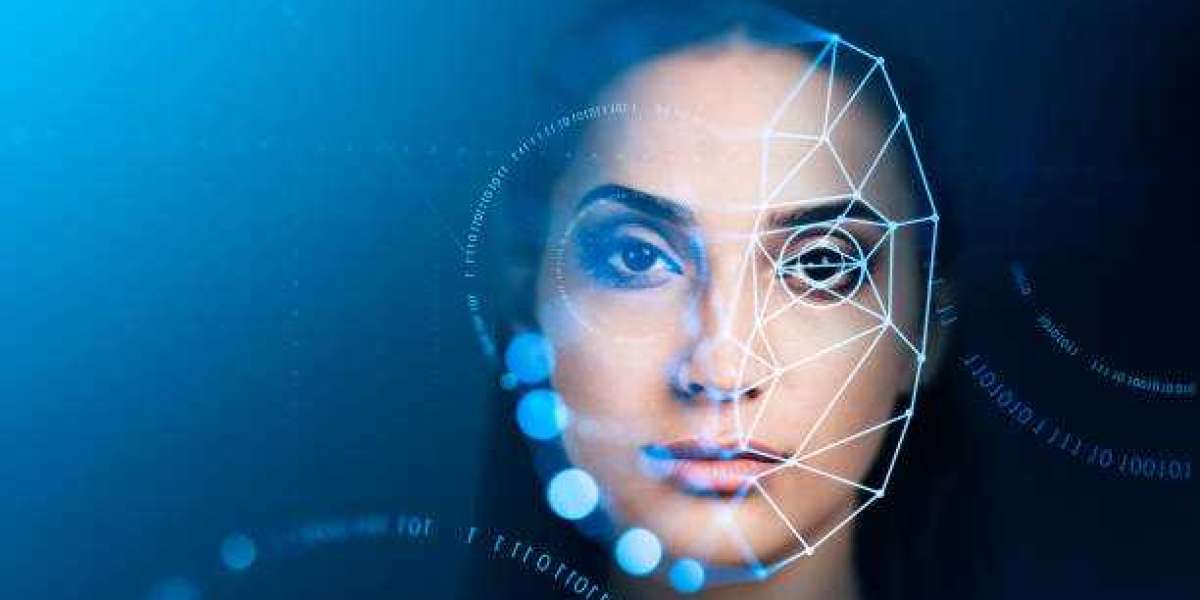
Face recognition is a biometric technology that identifies or verifies individuals based on facial features. This technology has evolved significantly with advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning, making it one of the most widely used and debated forms of biometric authentication. It operates by analyzing facial structures and comparing them to stored data to determine identity.
Importance and Relevance in Today's World
Face recognition has gained prominence due to its applications in security, law enforcement, and personal authentication. Governments and private organizations use it for surveillance, identity verification, and fraud prevention. Despite its advantages, concerns related to privacy, ethical implications, and potential misuse persist, making it a subject of discussion worldwide.
2. Technology Behind Face Recognition
How Face Recognition Works
Face Recognition follows a sequence of steps to identify or verify a person:
Face Detection: Identifying a face in an image or video.
Feature Extraction: Analyzing key facial features, such as distance between eyes, nose shape, and jawline.
Face Matching: Comparing extracted features with stored data in a database.
Decision Making: Determining a match based on similarity scores.
Key Components (Image Processing, Feature Extraction, Matching)
Face recognition technology relies on:
Image Processing: Enhancing image quality for better recognition.
Feature Extraction: Identifying distinctive facial features.
Matching Algorithm: Comparing extracted features with a reference database.
Machine Learning Models: Improving recognition accuracy over time.
Role of Artificial Intelligence and Deep Learning
AI and deep learning have significantly improved face recognition accuracy. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and deep learning models help in:
Identifying complex patterns in facial structures.
Reducing false positives and improving recognition under different lighting conditions.
Enhancing real-time processing capabilities.
Popular Algorithms and Models (e.g., CNNs, Eigenfaces, LBP, FaceNet)
Several face recognition algorithms and models contribute to its effectiveness:
Eigenfaces: Uses Principal Component Analysis (PCA) for feature reduction.
Local Binary Patterns (LBP): Captures texture-based features.
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Extracts deep features for high accuracy.
FaceNet: Uses deep learning for efficient face embeddings and comparisons.
3. Applications of Face Recognition
Security and Surveillance
Face recognition plays a vital role in security systems, helping law enforcement agencies monitor public spaces and detect unauthorized individuals. Airports, public transport systems, and government buildings use it to enhance security measures.
Law Enforcement and Crime Prevention
Police departments use face recognition to identify suspects and missing persons. It aids in criminal investigations by matching faces against databases of known offenders.
Mobile Devices and Authentication
Smartphones and laptops integrate face recognition for secure access. Apple's Face ID and similar technologies provide users with biometric authentication for unlocking devices and authorizing payments.
Healthcare and Patient Identification
Hospitals utilize face recognition to maintain patient records, prevent identity fraud, and streamline check-in processes. It ensures that patients receive accurate medical care based on their identity.
Retail and Customer Experience
Retailers use face recognition to personalize shopping experiences. Stores analyze customer preferences and provide tailored recommendations based on facial recognition data.
Banking and Financial Services
Banks implement Face Recognition Technology for fraud prevention, secure transactions, and identity verification. It enhances security in online banking and ATM transactions.
Smart Cities and Public Safety
Face recognition contributes to smart city initiatives by monitoring public areas, controlling access to restricted zones, and assisting in emergency response efforts.
4. Challenges and Limitations
Accuracy and Performance Issues
Face recognition systems can struggle with variations in lighting, facial expressions, and angles. Factors such as occlusions (e.g., glasses, masks) can impact accuracy, leading to false positives or negatives.
Privacy Concerns and Ethical Considerations
Privacy remains a major concern as face recognition technology collects and stores biometric data. Unauthorized surveillance and potential misuse of personal data raise ethical questions regarding individual rights and freedoms.
Bias and Fairness in AI Models
Face recognition algorithms have shown biases in accuracy across different demographic groups. Studies indicate that certain AI models perform better for certain ethnicities and genders, leading to disparities in identification accuracy.
Vulnerabilities (Spoofing, Deepfakes, Adversarial Attacks)
Face recognition systems are vulnerable to spoofing attacks using photos, videos, or masks. Deepfake technology can manipulate facial data, making it challenging to distinguish real identities from fake ones.
Legal and Regulatory Issues
Governments worldwide are introducing regulations to govern the use of face recognition. GDPR in Europe and laws in the U.S. and other countries impose restrictions on data collection and require transparency in the deployment of biometric technologies.
5. Future Trends in Face Recognition
Advancements in AI and Deep Learning
Ongoing research aims to enhance face recognition accuracy and efficiency. AI advancements will likely reduce biases, improve feature extraction, and enable real-time recognition.
Improved Privacy-Preserving Techniques (e.g., Federated Learning)
Techniques such as federated learning allow AI models to learn from decentralized data without compromising user privacy. This ensures better security and compliance with data protection regulations.
Integration with Other Biometric Technologies
Combining face recognition with other biometric methods (fingerprint, iris scanning, voice recognition) can enhance security and reduce false positives, leading to more robust authentication systems.
Government Regulations and Policy Developments
As Face Recognition System becomes widespread, governments will introduce policies to regulate its use. Striking a balance between security and privacy will be crucial in shaping its future deployment.
6. Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Face recognition technology has revolutionized security, authentication, and customer experiences. It leverages AI and deep learning to improve accuracy and efficiency but faces challenges related to privacy, bias, and ethical concerns.
The Future of Face Recognition
The future of face recognition lies in enhancing accuracy, reducing biases, and ensuring ethical implementation. Innovations in AI, privacy-preserving techniques, and regulatory frameworks will determine how society adopts and benefits from this technology in the years to come.